
NASA’s BioSCape Project to assess Cape Floristic Region
NASA’s BioSCape Project to test remotely sensed data to assess Cape Floristic Region biodiversity
By Andrew Turner, CapeNature Restoration Ecologist.
The South Western Cape hosts a famously rich biodiversity, both terrestrial and marine, which is largely derived from the phenomenal levels of biodiversity change over very small distances (technically, represented by beta, gamma and zeta diversity as one expands spatial scope). This has attracted the attention of NASA, the United States of America’s Space Agency. NASA will be flying two specially equipped jets in the Western Cape in 2023 as part of the BioSCape project involving multiple research and conservation collaborators. This is quite unlike what most of us think of as a NASA mission, as their focus will not be on outer space, but on the earth’s surface and on the living elements in particular. This is part of an increasing recognition that biodiversity is a key ingredient for environmental resilience, function and sustainability at all scales from local to global.
This cutting edge research will be tackled using hyperspectral sensors which, unlike most current satellite-derived data, can scan a big section of the electro-magnetic spectrum from 380 nano metres to 12 micro metres. If there are any wavelengths that are informative in characterising vegetation patterns these sensors should be able to pick them up. They will also be making use of light detection and ranging (LIDAR), which is similar in concept to RADAR, but uses laser light to establish the heights of the earth’s surface features so that accurate 3D surfaces can be mapped. The main objective of this study is to see if this new method of Earth Observation can be related to ground-based biodiversity patterns. If this turns out to be the case, it will improve our ability to survey wide swathes of the planet and assess and predict biodiversity health.
CapeNature’s Protected Areas represent both the diversity of the Cape Floristic Region and surrounds, its change across landscapes, the numerous key natural ecological processes such as fire, and the not so natural impacts of invasive alien species. This representation provides an ideal opportunity to test the theory of tracking biodiversity from remotely-sensed data. On the ground we can quantify biodiversity in rigorous and detailed ways that we are currently seldom able to achieve. Knowing what is happening with biodiversity can inform us about what is happening with ecosystem processes. The focus for the Western Cape will be water availability, fire and invasive alien species. For example, it will be very interesting to see how well the new imagery can represent invasive alien species and groundwater dependent ecosystems. One of the proposals even includes collecting automated sound data so that we can assess a very different way of quantifying biodiversity that may be hard to see, but easy to hear. All of these systems are dynamic and there are constant changes in land-use and climate change. Getting this detailed window on biodiversity patterns is going to be invaluable to measure and evaluate environmental change in future when this means of data may become more easily accessible via satellite.
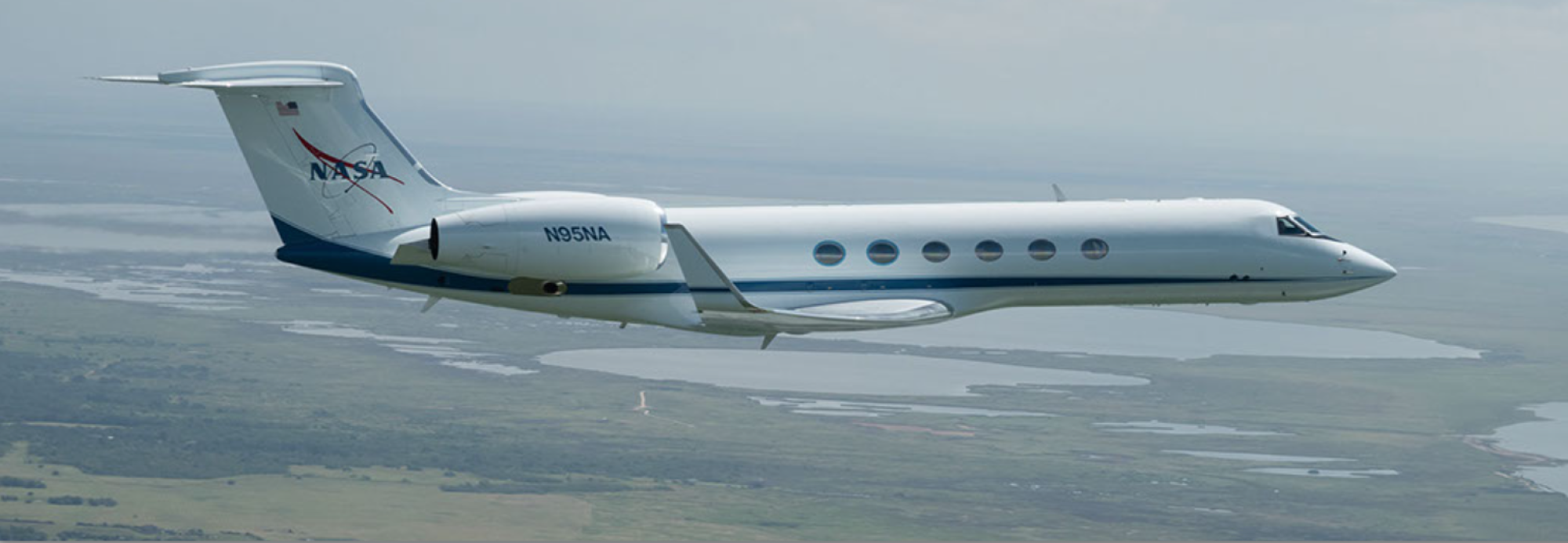

Picture 1: One of the specially-equipped NASA aircraft. Credit: Johnson Space Centre.
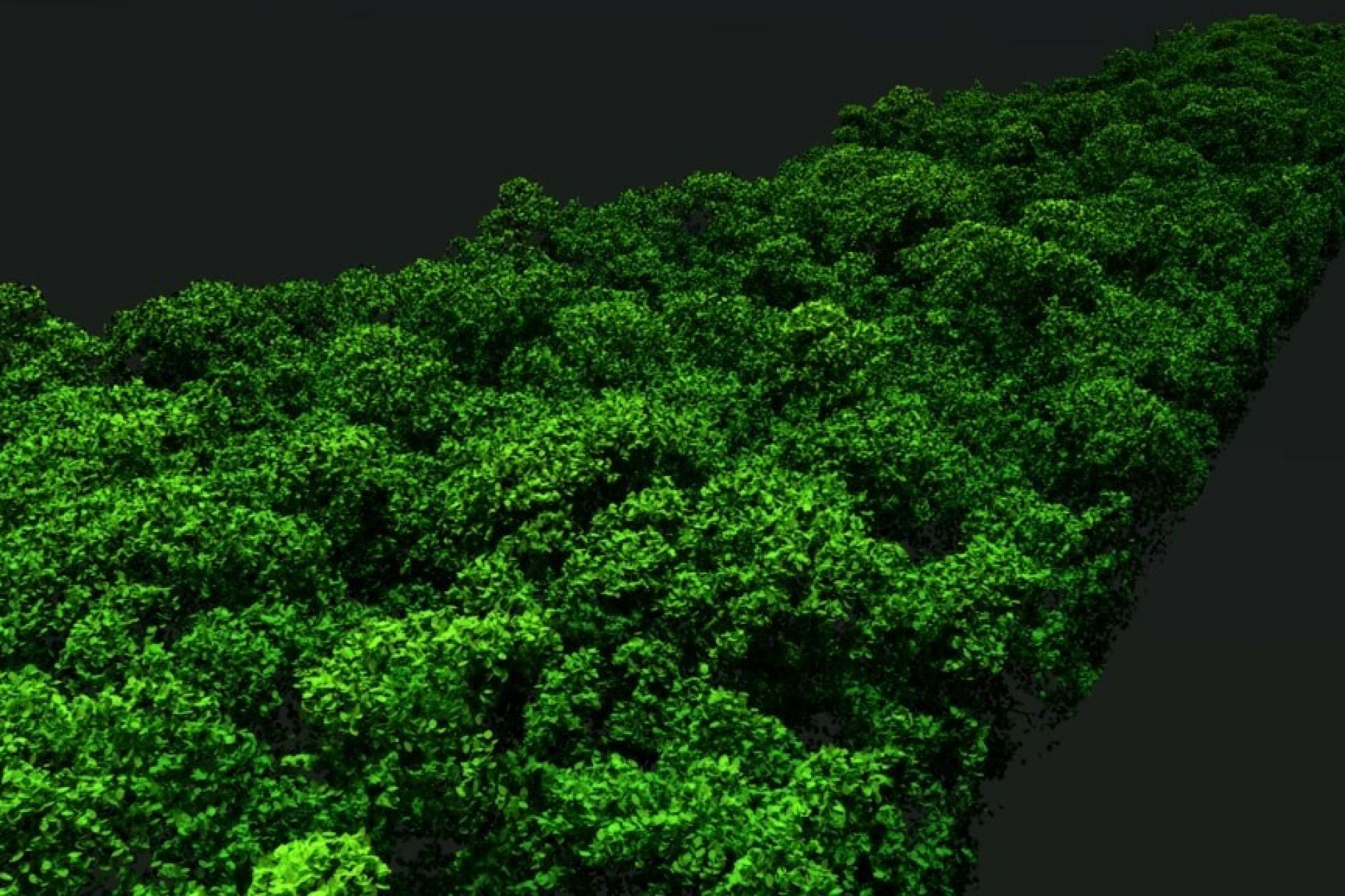
Picture 2: A LIDAR image of vegetation displaying an example of the 3d point cloud imagery obtainbable with this technology. Credit: NASA.




