
Record-breaking pine clearing operation strengthens water security at Boosmansbos
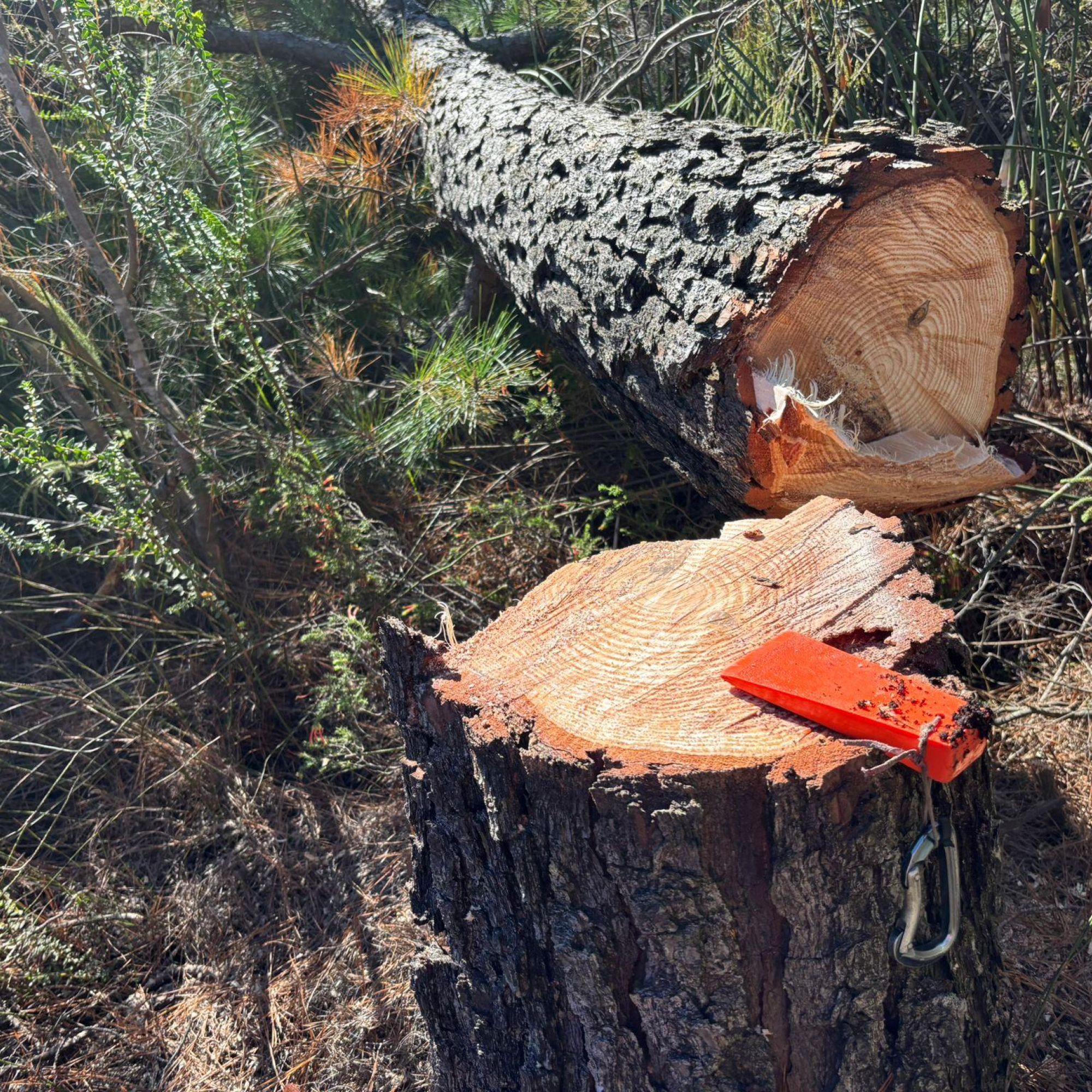
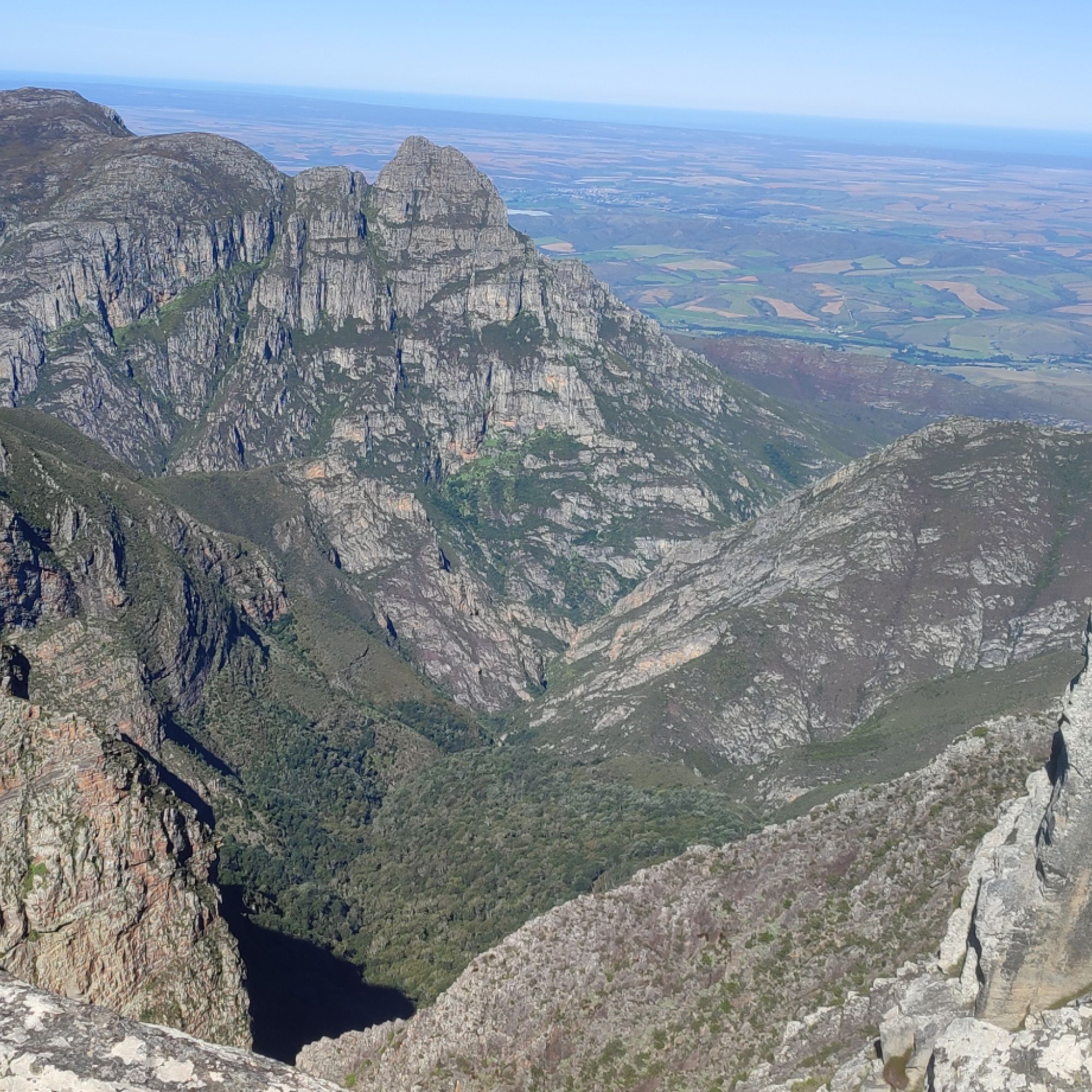
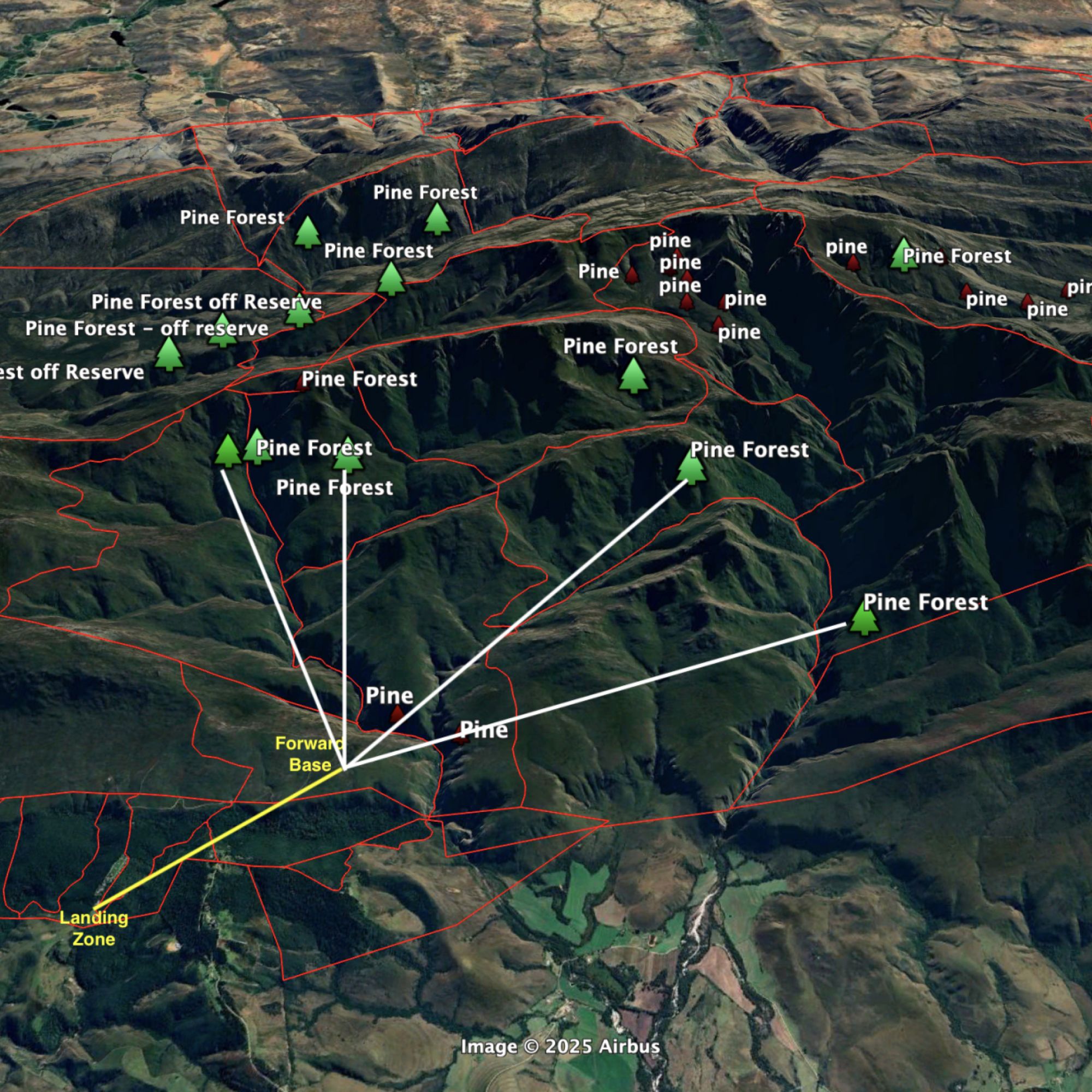
A successful HeliHack operation has cleared 15 194 invasive pine trees from the rugged slopes of the Boosmansbos Wilderness Area – a CapeNature-managed World Heritage Site and crucial catchment area feeding the Duivenhoks Dam.
From 3–5 May 2025, the latest mission to tackle the invasive alien vegetation marked the most successful pine removal in the initiative’s history.
Located in the Grootvadersbosch complex and forming part of the Langeberg Strategic Water Source Area, Boosmansbos plays a pivotal role in water security for approximately 15 000 residents of Heidelberg, Slangrivier, Witsand and surrounding farms.
Invasive pine trees in the broader catchment are a major threat to both biodiversity and water supply, draining critical resources and intensifying wildfire risk.
Invasive alien plants are estimated to consume over 7% of South Africa’s water resources. Effective catchment management and restoration can increase streamflow by 15–30%, offering measurable benefits for people and ecosystems.
As a provincial government, we recognise that our natural ecosystems, such as our rivers, wetlands, forests, and catchments are the foundation of water and food security, economic opportunity, and public wellbeing. By clearing invasive species, we are actively strengthening the resilience of our Province’s natural infrastructure. These operations not only solve today’s issues but help to prepare the Province for the future. A future-fit Western Cape will help to protect our communities against the impacts of climate change and help to maintain a thriving biodiversity where natural resources are managed responsibly.
Over just three days, 21 volunteers, supported by a helicopter crew, tackled decades-old pines rooted deep within the steep western slopes above the Duivenhoks River. The results were immense: 15 194 pines removed, 1 080 hectares covered, and 12.8 helicopter hours flown.
The May 2025 operation surpasses all previous HeliHack missions, bringing the cumulative totals to 26 913 pines cleared, 3 880 hectares restored, and 27% of Boosmansbos Wilderness Area cleared.
The scope of CapeNature’s work would not be possible if we only worked in silos. The Entity relies on the support of many partners to achieve our work and HeliHack is one such example of our successful collaborations. We’re securing water, protecting biodiversity, and building resilience for the future. Conservation gains are only sustainable in the long-term when government and citizens partner to innovate and implement.
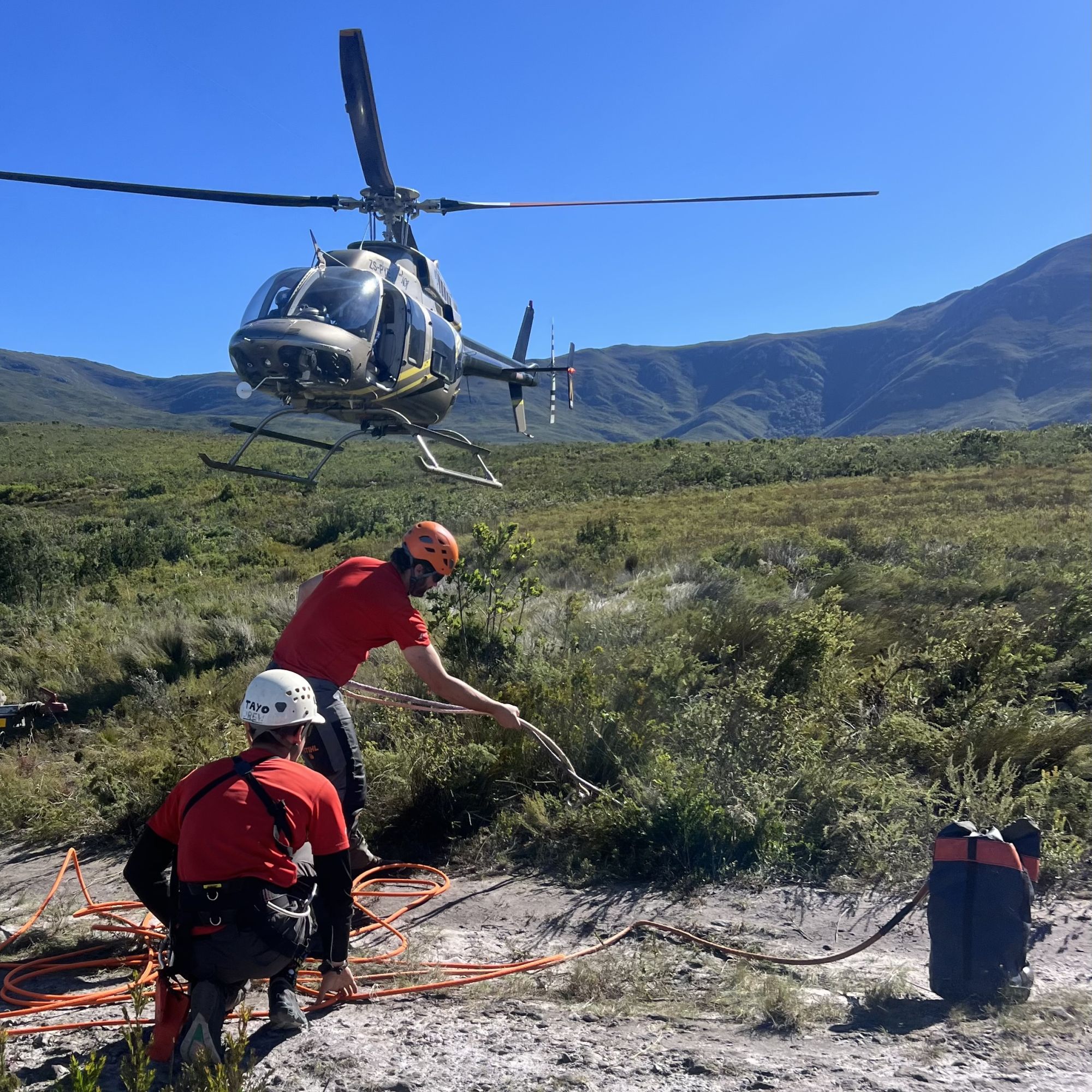



Boosmansbos, which spans 14 200 hectares, is not only a biodiversity stronghold but also a natural support for sustainable water supply. With climate change heightening pressure on water systems, innovative operations like HeliHack are essential in keeping catchments resilient.
You look down at those ancient pines on impossible slopes, and you know this is the only way to get them out. The precision and teamwork required for HeliHack are immense, and the results speak for themselves.
Every pine removed by HeliHack is a win for the Boosmansbos ecosystem. This operation is tangible proof that strategic, innovative conservation can make a profound difference for our natural heritage.



The HeliHack initiative also made the rediscovery of the elusive Boosmansbos long-tailed forest shrew possible. Conservationists from CapeNature, Grootvadersbosch Conservancy and volunteer biologists, worked alongside the HeliHack teams in the remote mountain peaks to confirm the continued existence of this tiny Critically Endangered species after 46 years of looking for it.
Read more about the long-tailed forest shrew that was last discovered 46 years ago.
CapeNature formalised its commitment to the HeliHack Project in 2024, expanding the initiative’s scope within Boosmansbos and across four additional Provincial Nature Reserves. This partnership signals an investment in innovation-led conservation, reinforcing CapeNature’s role as a custodian of the Western Cape’s natural heritage and the Cape Floristic Region.




